Exploring Remote IoT P2P Examples: Direct Connections For A Smarter Future
Have you ever thought about how your smart devices talk to each other, especially when you're not even home? It's a pretty interesting question, that. Typically, many of our connected gadgets rely on big central servers in the cloud to send and receive information. This setup, while common, can sometimes mean slower responses, potential privacy worries, and a bit of a higher cost. For instance, you might use an app on your phone to turn on a light at home, and that command usually travels all the way to a cloud server and then back down to your light.
But what if there was a different way for these devices to chat? What if they could just speak directly to one another, or to you, without needing a middleman? This is where the idea of peer-to-peer (P2P) communication comes into play for the Internet of Things, or IoT. It's a way for devices to form direct links, making things feel a lot more personal, so to speak, in how they interact.
Thinking about remote access, like when you securely access your computer whenever you're away, using your phone, tablet, or another computer, the P2P approach for IoT brings a similar kind of directness. It's about letting your smart devices connect with you, or with each other, even when you are far away, without always bouncing data off a distant server. This can make everything feel a bit snappier and perhaps even more secure. We will look at some remote IoT P2P examples and see how they are changing things.
Table of Contents
- What is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) in IoT?
- Why P2P Matters for Remote IoT
- Real-World Remote IoT P2P Examples
- Challenges and Considerations
- The Future of Remote IoT P2P
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) in IoT?
Peer-to-peer, or P2P, in the world of IoT means that devices can communicate directly with each other without needing a central server to manage every single interaction. Think of it like a group of friends chatting directly, rather than needing to send every message through a single, shared mailbox. This direct communication path is a bit different from what many people are used to, so.
Traditional vs. P2P IoT
In a typical IoT setup, your smart thermostat, your security camera, and your phone all send their data to a cloud server. That server then processes the information and sends commands back. So, if your phone wants to see what your camera sees, the video stream goes from the camera to the cloud, and then from the cloud to your phone. This works, of course, but it adds steps and potential points where things could slow down or face issues.
With P2P, however, the camera might send its video directly to your phone. This means a more direct line of communication, which can be very beneficial for certain uses. It's a shift from a hub-and-spoke model to a more distributed network, where each device, or "peer," has the ability to connect with others. This can make things feel a bit more streamlined, and perhaps even more personal for the devices involved, in a way.
- Faith Adanza Sex
- Iot P2p Connect Free
- Onlyfans Leaks Lia Engel
- Abby Berner Leaks
- V3 Vegamovies.bitbucket.io
How P2P Works for Remote Access
For remote access, P2P in IoT is about creating a direct channel between your remote device (like your phone) and a smart device at your location (like a smart lock). Instead of your command traveling to a cloud server and then to the lock, your phone tries to establish a direct connection to the lock. This is similar to how you might use remote desktop on your windows, android, or ios device to connect to a windows pc from afar, where the connection is meant to be as direct as possible.
This direct connection often involves some clever tricks to get past network firewalls, like "hole punching" or using relay servers only for the initial connection setup, not for the ongoing data transfer. Once the direct link is made, the data flows straight between the two points. This approach can really cut down on delays and make interactions feel much more immediate, which is quite nice for remote control.
Why P2P Matters for Remote IoT
The P2P approach brings several important advantages to remote IoT, making it a compelling option for many applications. These benefits touch on things like safety, speed, and even how much things cost, which is pretty significant.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
When data travels directly between devices, it often bypasses central servers that could be targets for large-scale data breaches. This means your private information, like video feeds from your home security cameras or health data from a wearable, stays more contained. It's a bit like having a private conversation directly with someone instead of shouting it across a crowded room. This can offer a greater sense of security and privacy, which is very important in today's connected world.
Because the data doesn't sit on a third-party server, there are fewer points where it could be intercepted or misused. This direct path can reduce the risk of sensitive information being exposed, giving users more control over their own data. It feels a bit more personal, in a good way, for your data to stay close to home, so to speak.
Reduced Latency and Improved Performance
Cutting out the middleman – the cloud server – means data has a shorter distance to travel. This leads to significantly reduced latency, or delay, in communication. For things like remote control of machinery, live video streaming, or even just turning on a light switch, quicker response times make a huge difference. Imagine trying to steer a drone remotely; every millisecond of delay matters, you know?
Improved performance isn't just about speed; it's also about responsiveness. When your devices react almost instantly, the user experience is much smoother and more natural. This is particularly true for applications where real-time interaction is crucial, making the system feel more alive and connected.
Cost Savings and Scalability
Operating large cloud infrastructures can be quite expensive, especially as the number of connected devices grows. With P2P, the need for extensive server resources is lessened, as much of the data processing and routing happens at the "edge" – on the devices themselves. This can lead to considerable cost savings for both service providers and users over time, which is pretty neat.
Scalability also gets a boost. Instead of a central server becoming a bottleneck as more devices join the network, a P2P system can expand more naturally. Each new device adds to the network's capacity rather than just increasing the load on a central point. This makes it easier to grow the system without constantly upgrading server infrastructure, which is a big plus for future development.
Reliability and Offline Capability
If a central cloud server goes down, all devices relying on it might stop working. A P2P network, however, is often more resilient. If one device or connection fails, others can still communicate. This distributed nature means there's no single point of failure, making the system more robust and dependable, which is very reassuring.
Furthermore, some P2P setups can allow devices to continue communicating even if the internet connection to the outside world is lost. For example, smart home devices might still talk to each other within the local network, even if they can't reach the cloud. This "offline capability" is a significant advantage for critical applications where continuous operation is a must, like security systems or health monitors.
Real-World Remote IoT P2P Examples
Seeing P2P in action helps us understand its real value. There are several areas where this direct communication approach is already making a noticeable impact, or where its potential is truly exciting. These examples show how devices can talk directly, even when they are far apart, which is pretty cool.
Smart Home Automation
Imagine a smart home where your security camera sends a live video feed directly to your phone when motion is detected, without routing through a cloud server. Or perhaps your smart door lock communicates directly with your smart doorbell to verify who's at the door. These are excellent remote IoT P2P examples. When you are away, you can still securely check on your home, perhaps even letting someone in, with that direct connection making things feel much safer.
Another instance could be a smart thermostat adjusting based on direct input from window sensors, all without needing an internet connection for their basic functions. This local, direct interaction improves privacy and ensures functionality even during internet outages. It's about giving you a more immediate and private way to manage your home from afar, much like how you would connect to a Windows PC from afar using remote desktop.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Monitoring
In factories and industrial settings, machines need to communicate rapidly and reliably. P2P connections can allow sensors on a production line to send data directly to a control system or to other machines for immediate adjustments. This reduces the delay that cloud processing might introduce, which is critical for safety and efficiency in fast-moving operations.
For remote monitoring, a technician could directly access sensor data from a piece of machinery in a distant plant, getting real-time insights without data needing to travel through multiple cloud layers. This direct access can help with predictive maintenance and quick problem-solving, making operations smoother and more reliable, you know?
Remote Health Monitoring
Wearable health devices could use P2P to send vital signs directly to a patient's family member's phone or a local care provider's tablet, especially in situations where a constant, secure, and low-latency connection is paramount. This can be incredibly important for elderly care or for monitoring chronic conditions, where every second counts.
This direct data transfer minimizes the risk of sensitive health information being exposed on third-party servers, offering a higher degree of privacy. It also means quicker alerts and responses in emergency situations, making remote care feel much more immediate and trustworthy, which is a huge benefit for patients and their families.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
In the future of connected vehicles, P2P communication will be vital. Cars will need to talk directly to each other (vehicle-to-vehicle, V2V) to avoid collisions, share traffic information, and coordinate movements. They will also need to communicate with traffic lights, road sensors, and even pedestrians' devices (vehicle-to-infrastructure, V2I, and vehicle-to-pedestrian, V2P). This direct communication is essential for immediate reactions and safety.
This direct, low-latency communication is crucial for autonomous driving and smart city initiatives. For example, a car could receive an immediate warning about black ice ahead from another car that just passed over it, rather than waiting for that information to be processed by a central system. This kind of immediate, direct data sharing is a key remote IoT P2P example for future transportation.
Challenges and Considerations
While P2P offers many exciting possibilities for remote IoT, it's not without its own set of hurdles. Getting devices to talk directly can sometimes be a bit tricky, and there are important things to think about to make it work well.
Discovery and Connectivity
One of the main challenges is how devices find each other on a network, especially when they are far apart or behind different firewalls. It's like trying to find a specific friend in a huge, unfamiliar city without a central directory. Techniques like "hole punching" or using temporary relay servers help establish the initial connection, but setting this up reliably across diverse network environments can be complex.
Maintaining a stable direct connection, especially over long distances or through varying network conditions, also presents difficulties. Devices might move, IP addresses might change, or network configurations could shift. Ensuring consistent connectivity requires clever engineering and robust protocols, so it's not always a straightforward path.
Security Best Practices
Even though P2P can enhance privacy by reducing reliance on central servers, it still requires strong security measures. Each direct connection needs to be properly authenticated and encrypted to prevent unauthorized access or data tampering. Without a central authority to manage security, each device must be capable of handling its own security protocols, which is a big responsibility.
Implementing proper key management, secure device onboarding, and regular security updates across a distributed network of devices can be quite a task. It's important to make sure that every "peer" in the network is trustworthy and that their communication lines are well-protected, which is pretty vital.
Standardization
For P2P IoT to truly flourish, there needs to be more agreement on common standards and protocols. Currently, different manufacturers and platforms might use their own proprietary methods for P2P communication, making it harder for devices from different brands to talk to each other directly. This lack of universal language can slow down widespread adoption, in some respects.
Developing and adopting open standards would allow for greater interoperability, meaning devices from various makers could seamlessly connect and interact. This would foster a more collaborative and expansive IoT ecosystem, making it easier for everyone to build and use P2P solutions. It's a bit like needing a common language for everyone to understand each other, you know?
The Future of Remote IoT P2P
The trend towards edge computing, where data processing happens closer to the source rather than in distant clouds, strongly supports the growth of P2P in IoT. As more intelligence is built into the devices themselves, their ability to communicate directly and autonomously will become even more pronounced. This shift promises a future where our devices are not just connected, but truly interconnected, in a way that feels more natural and efficient.
We are likely to see more innovative remote IoT P2P examples emerge, especially in areas requiring high security, low latency, and operational independence. From smarter cities where infrastructure components communicate directly, to more personalized healthcare solutions, the possibilities are vast. This direct communication will enable new kinds of services and experiences, making our interactions with technology much more immediate and reliable, which is a really exciting prospect for what is to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is P2P in IoT?
P2P in IoT means that connected devices, like smart sensors or cameras, can talk directly to each other or to a user's device without needing a central cloud server to manage every single message. It's about creating direct lines of communication between individual "peers" in the network.
Why is P2P important for IoT devices?
P2P is important for IoT devices because it can offer better security and privacy by keeping data off central servers. It also helps reduce delays, improves performance, saves on infrastructure costs, and makes systems more reliable, especially for remote access or real-time needs.
Can IoT devices communicate without the internet?
Yes, many IoT devices can communicate without an internet connection, especially if they are using P2P or local network protocols like Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Wi-Fi Direct. This allows them to function within a home or local area even if the main internet connection is down, which is quite useful.
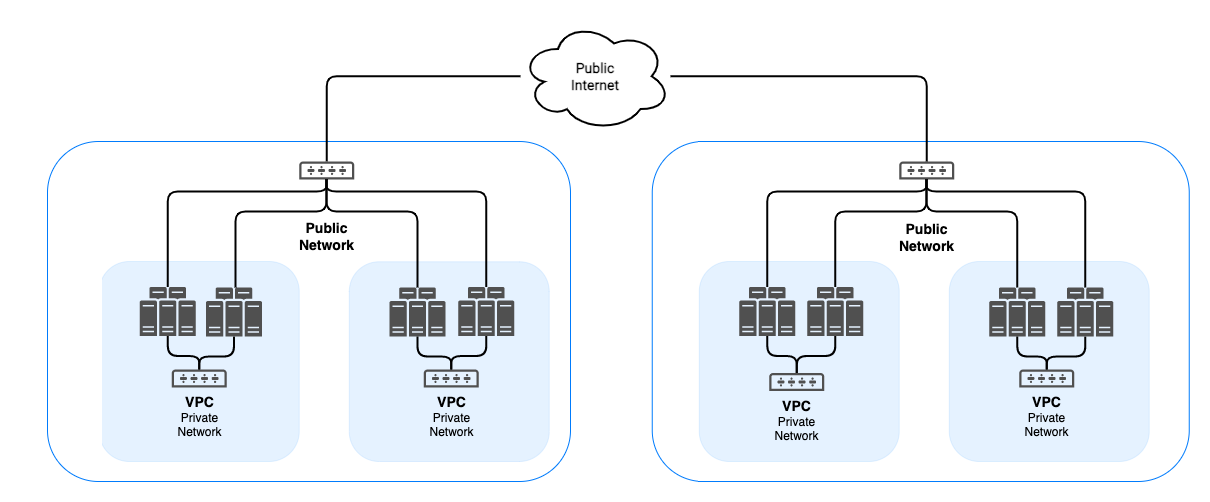
Securely Connect Remote IoT P2P SSH Raspberry Pi Free Server
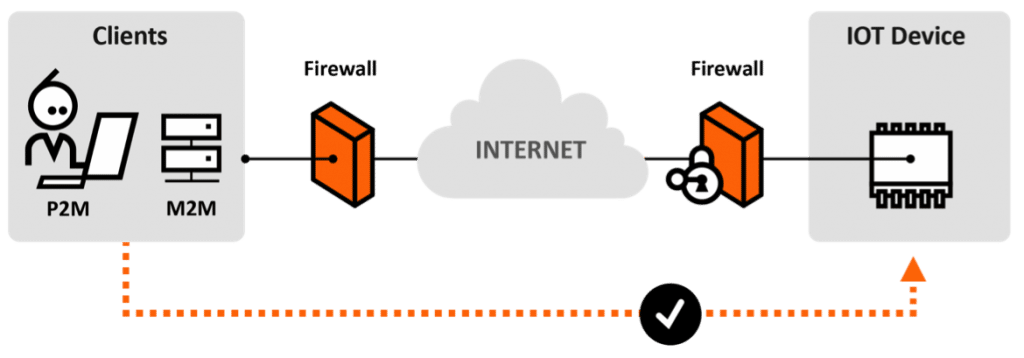
P2P IoT Connectivity Solution for Remote Control of Devices

Mastering Secure IoT Connections: A Step-by-Step SSH Guide For Ubuntu