Getting Connected: Your SSH Remote IoT Example Guide For Today
Connecting to faraway devices, especially for your smart home gadgets or industrial sensors, can sometimes feel a bit like trying to talk across a really big room. You want a clear line, something safe and sound. This is where a method called SSH, or Secure Shell, truly shines, offering a way to chat with your Internet of Things (IoT) devices no matter where they are. It’s a pretty big deal for anyone wanting to keep an eye on things from afar, or even send new instructions.
Think about managing your smart garden's watering system from your office, or checking on a sensor in a remote power station. You need a secure pathway for that information. SSH gives you that private conversation channel, so your data stays just between your computer and the device. It’s about making sure only you, or people you trust, can get in there, which is, you know, a very good thing.
This guide will walk you through what SSH means for your remote IoT setup. We'll look at some common situations, talk about how to keep things secure with special keys, and even touch on what to do when things don't quite go as planned. You’ll get a pretty good idea of how to make your remote IoT connections work smoothly, and stuff.
- Pinay Scandal News 2024 Philippines
- Howard Morley Oregon
- V3 Vegamovies.bitbucket.io
- How Much Does Patience Wolfe Make
- Viralkamd
Table of Contents
- What is SSH for IoT?
- Why SSH Matters for Remote Devices
- Setting Up Your SSH Remote IoT Example
- Moving Files Around with SSH
- Common SSH Remote IoT Challenges
- Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT
- Making Your Remote IoT Connections Work
What is SSH for IoT?
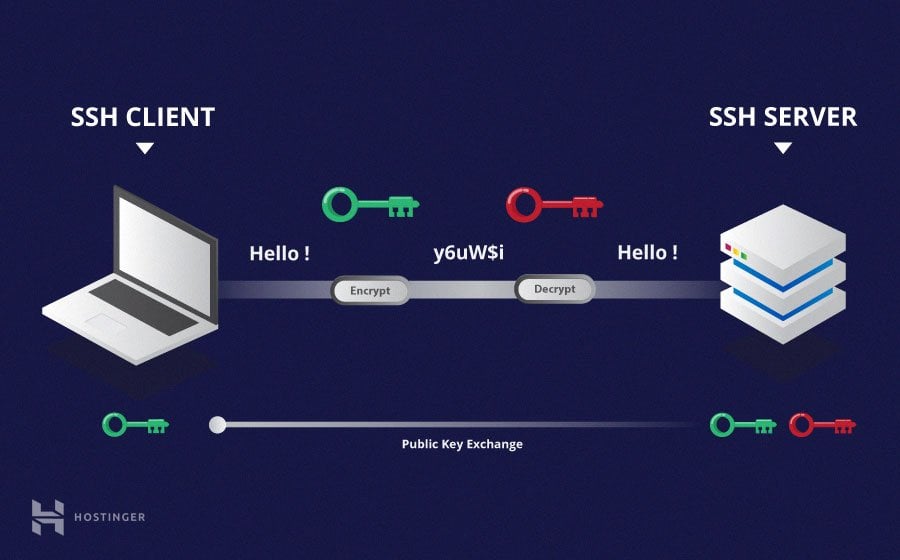
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a way to access and manage computers over an unsecured network. It provides a strong, encrypted path for sending commands and data. For IoT devices, this means you can get to them from anywhere, even if they are miles away. It's like having a secure, direct line to your smart gadgets.
When we talk about an ssh remoteiot example, we mean using this secure connection for your little internet-connected things. These could be anything from a tiny sensor in a field to a camera watching your front door. You want to make sure no one can listen in or mess with your devices, so SSH is very helpful here.
It's all about keeping your remote interactions private and safe. This is especially true as more and more devices get online, so, you know, security becomes a bigger deal. Using SSH helps keep those connections locked down, which is really quite important.
Why SSH Matters for Remote Devices
The number of devices connecting to the internet is growing pretty fast, actually. From smart home setups to big industrial systems, everything seems to be getting connected. This trend means we need solid ways to talk to these devices from afar. SSH gives us that strong, safe link, which is kind of essential.
Imagine you have a device that collects weather data out in a remote spot. You need to pull that data, or maybe update the device's software. SSH lets you do this without having to physically go there. It saves time and effort, and that's a big win for managing many devices, or so it seems.
Beyond just getting access, SSH protects the information you send and receive. It makes sure that when you tell your device to do something, only your device hears it. This protection is a very big reason why so many people use SSH for their remote IoT work, just to be on the safe side.
Setting Up Your SSH Remote IoT Example
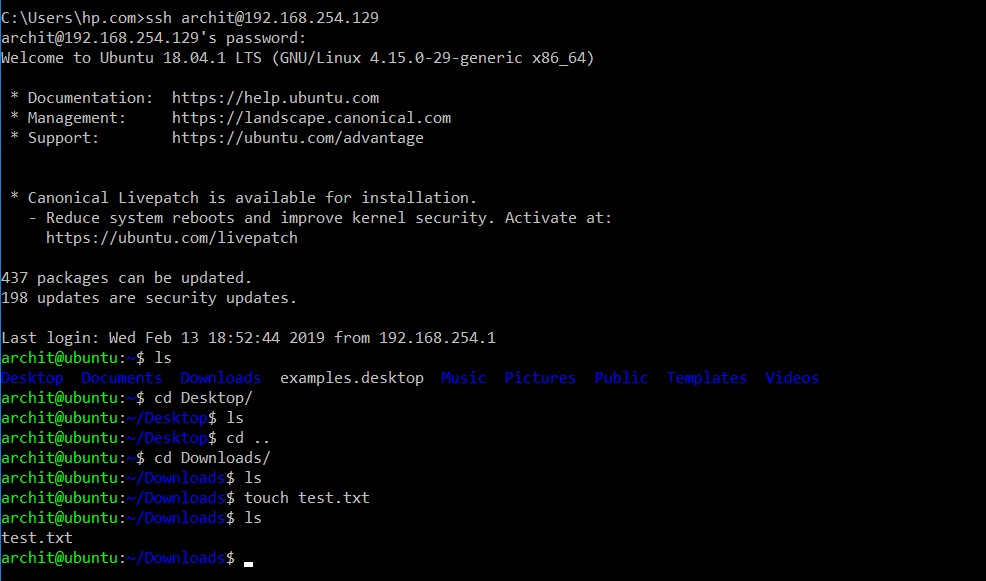
Getting your first SSH connection going for an IoT device is usually pretty straightforward. You'll need the device's network address and a way to log in. Often, this involves a username and password, or better yet, a special key. This key system is really what makes SSH so secure, you know.
For a basic setup, you might just open your computer's terminal program. Then you type a command like `ssh username@device_ip_address`. This tells your computer to try and make a secure connection. If everything is set up right, you'll be prompted for a password or your key will do the work, and you'll be in, more or less.
It’s important to make sure your IoT device is ready to accept SSH connections. Some devices might need you to turn on this feature in their settings. Others might have it ready to go from the start. Checking your device's instructions is always a good first step, obviously.
Creating and Managing SSH Keys
Using SSH keys is a much safer way to connect than just using passwords. A key pair has two parts: a private key that stays on your computer and a public key that goes on the remote device. When you try to connect, these two keys check each other, like a secret handshake, which is pretty neat.
My text talks about creating a specific key pair for a proxy server, not just using the default `id_rsa` key. This is a smart move for security. It means if one key gets into the wrong hands, your other connections are still safe. You can make new keys with a command like `ssh-keygen`, which is fairly simple.
Once you have your public key, you need to get it onto your IoT device. A common way is to copy it to a file called `authorized_keys` in the device's SSH folder. My text mentions copying a public key to a clipboard using `pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub` and then adding it to GitHub settings. This shows how public keys are shared to allow access, and it's basically the same idea for your IoT device, too.
Keeping your private keys safe is super important. They should never leave your computer. Some systems, like macOS, let you add your identity to a keychain, as @dennis pointed out in my text. This helps keep your key ready for use without having to type a password every time, and it makes it persist, which is nice.
Connecting to a Proxy Server
Sometimes, your IoT device might not be directly reachable from the internet. It might be behind a firewall or on a private network. In these cases, you might connect through a proxy server first. This server acts as a middleman, forwarding your SSH connection to the actual device, so it's a bit like a stepping stone.
My text mentions connecting to an SSH proxy server using a specific key pair. This setup adds another layer of security and network organization. You connect to the proxy, and then the proxy connects to your IoT device. It’s a common way to manage access to devices that are not directly exposed to the outside world, you know.
To set this up, you might configure your SSH client to use a `ProxyCommand` in your SSH configuration file. This tells your computer how to reach the proxy, and then how to go through it to your final destination. It's a slightly more complex setup, but it gives you a lot more control over your connections, and stuff.
Moving Files Around with SSH
One of the most useful things you can do with SSH for IoT is to move files. You might need to send a new program to your device, or pull log files from it. My text asks about copying an entire directory from a local machine to a remote machine. This is a very common task, actually.
The `scp` command (Secure Copy Protocol) is your friend here. It uses SSH to securely transfer files and folders. To copy a directory from your local machine to a remote IoT device, you would use a command like `scp -r /local/path/to/directory username@remote_ip:/remote/path/`. The `-r` part means "recursive," so it copies everything inside the folder, too.
Similarly, if you need to get files from your IoT device back to your computer, you just flip the order. You'd use `scp -r username@remote_ip:/remote/path/to/directory /local/path/`. It's a pretty straightforward process once you get the hang of it. This capability is really helpful for managing your devices, especially for updates or data collection, you know.
Common SSH Remote IoT Challenges
Even with SSH being so helpful, you might run into some bumps along the way. My text mentions a few issues people face, like problems after changing an Apple ID password, or scripts returning an error code like 255. These are common things that happen, so it's good to know what to look for, more or less.
Sometimes, a connection just won't work, and you get a message saying the remote script returned 255. This usually means something went wrong on the device you're trying to connect to. It could be a script that failed, or a program that didn't run as expected. Checking the logs on the remote device is usually the first step to figure out what's going on, which is fairly typical.
Another issue might be related to your computer's own setup, especially after big changes. My text talks about updating an Apple ID and restarting a Mac, which then led to Git issues. SSH connections can be sensitive to changes in your system's security settings or key management. A fresh start or checking your local SSH configuration files can often fix these sorts of things, you know.
Dealing with Host Keys
When you connect to a new remote device using SSH, your computer remembers that device's unique host key. My text mentions, "Using ssh, every host has a key. Clients remember the host key associated with a particular address." This is a security measure. It helps make sure you're connecting to the right device and not some imposter, which is a good thing.
If the host key changes for a device you've connected to before, SSH will give you a warning. This often happens if the remote device was reinstalled or if its network address changed. While it can be a sign of trouble, it's usually just something you need to confirm. You might need to remove the old host key from your computer's `known_hosts` file to connect again, you know.
It's important to be careful when accepting new host keys. Always make sure you are connecting to the correct device. If you're unsure, it's better to investigate before proceeding. This little check helps keep your connections secure, and that's pretty much what SSH is all about, right?
Troubleshooting Connection Errors
Getting an error message like "remote script returns 255" can be a bit frustrating. This usually means the command you tried to run on the remote device didn't finish properly. My text asks, "How about showing us the script?" This is a very good question, actually.
To fix this, you often need to log into the remote device directly, if you can. Then, try running the script or command manually. This way, you can see any error messages that pop up on the device itself. It might be a missing file, a permission problem, or just a bug in the script. Looking at the device's logs can also give you clues, which is often very helpful.
For Git-related SSH issues, like the one in my text after installing Git and adding an SSH key to GitLab, the problem might be with your local SSH agent or the key itself. Sometimes, the key isn't loaded correctly, or the permissions on the key file are wrong. Checking your SSH agent status and making sure your key is added can often resolve these kinds of problems, and stuff.
X11 Forwarding and Display Issues
Sometimes, you might want to run a graphical application from your remote IoT device and see its window on your local computer. This is called X11 forwarding. My text mentions, "If you run ssh and display is not set, it means ssh is not forwarding the x11 connection." This is a specific feature that needs to be turned on, you know.
To make X11 forwarding work, you usually need to add the `-X` option when you connect via SSH, like `ssh -X username@device_ip_address`. My text also suggests checking for a line containing "requesting x11 forwarding" to confirm it's working. If it's not set, the graphical program won't be able to show its window on your screen, which is kind of annoying.
You also need to make sure X11 forwarding is allowed on the remote IoT device itself. This is usually a setting in the SSH server's configuration file. If everything is set up correctly on both ends, you can run a graphical tool on your IoT device and see it pop up on your computer, which is pretty neat for certain tasks, actually.
Frequently Asked Questions About SSH and IoT
People often have similar questions when they start using SSH for their remote devices. Here are a few common ones:
How do I fix a "remote script returns 255" error when using SSH for my IoT device?
This error often means something failed on the remote device itself. You should try to log into the device directly, if you can, and run the command or script again. Look for specific error messages that appear on the device's console. Checking system logs on the IoT device can also help you find out what went wrong. It's usually a problem with the script's code or its environment, you know.
Why do I need a special SSH key pair for a proxy server, not just my regular one?
Using a specific key pair for a proxy server adds an extra layer of security. If that specific key is ever compromised, only your connection to that proxy is at risk. Your other SSH connections, which use your default key, would still be safe. It's a way to limit potential damage and keep your overall system more secure, which is a very good practice, actually.
How can I copy an entire folder from my computer to a remote IoT device using SSH?
You can use the `scp` command for this. To copy a whole directory from your local machine to a remote IoT device, you'd open your terminal and type `scp -r /your/local/folder/path username@device_ip:/remote/destination/path/`. The `-r` part is important; it tells `scp` to copy everything inside the folder, including any subfolders and files. This is a very handy command, really.
Making Your Remote IoT Connections Work
Using SSH for your remote IoT devices gives you a powerful way to manage them securely. From setting up specific keys to moving files around, it provides a solid foundation for your remote operations. We've seen how important it is to manage your keys carefully and how to deal with common connection hiccups. It's all about making sure your devices are reachable and safe, which is a pretty big deal in today's connected world, you know.
Remember, the security of your IoT setup depends a lot on how well you handle your SSH keys and connections. Keeping your software up to date and regularly checking your configurations can help prevent many problems. If you run into issues, taking a calm, step-by-step approach to troubleshooting, like checking scripts or host keys, often leads to a solution, and stuff.
For more general information about securing your network, you might want to look at resources on network security best practices. Learn more about secure connections on our site, and link to this page here for further reading on remote access. Getting your remote IoT example running smoothly means you can focus on what your devices do best, whether it's collecting data or automating tasks, which is really the goal.
RemoteIoT SSH Free Download: Your Gateway To Secure Remote Access
Secure IoT Connections With SSH: A Beginner's Guide

Best SSH Remote IoT Free: Unlocking The Potential Of Secure IoT Connections