The Meaning Behind X*xxxx*x Is Equal: Discovering True Equivalence
Have you ever looked at a sequence like "x*xxxx*x" and wondered what it truly means when it's declared "equal"? It's a curious pattern, isn't it? This seemingly simple arrangement of symbols actually holds a surprising amount of depth, inviting us to consider how we perceive balance, identify consistent structures, and, in a way, sort through information to find what matches up. So, what, you might ask, makes this particular string of characters significant? Well, it's about much more than just a few letters and asterisks; it’s about the very heart of how we establish sameness or correspondence in a world full of different things.
This idea of something being "equal" to something else, especially when dealing with patterns like "x*xxxx*x", stretches across so many different areas of our daily lives, you know? From the way we organize information to the way systems operate, recognizing when things align perfectly or when they possess a shared characteristic is, basically, a fundamental skill. It's almost like a detective's work, trying to find those specific conditions that make one thing just like another, or at least, equivalent in a meaningful sense. We are, after all, always trying to make sense of things by seeing how they fit together.
In this discussion, we're going to take a closer look at what "x*xxxx*x is equal" can imply, exploring the various ways this concept shows up in different settings. We'll touch upon how we recognize these kinds of patterns, why identifying them matters, and how these ideas are, actually, quite important for making good choices and building reliable systems. It's really about getting a better grasp of the underlying principles that make things comparable, and how that helps us understand our world, you see.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Pattern: What Does x*xxxx*x Mean?
- Finding Equivalence in Data and Information
- Systems and Consistency: Where Equality Really Matters
- Human Perception of Sameness: More Than Just Numbers
- Common Questions About Patterns and Equality
Understanding the Pattern: What Does x*xxxx*x Mean?
When we look at "x*xxxx*x," the first thing that probably comes to mind is a kind of placeholder, isn't it? The 'x' often stands for something variable, while the asterisks might represent any number of other characters or elements. So, when someone says "x*xxxx*x is equal," they're not just talking about a literal string of characters being identical. They're usually pointing to a condition where a specific pattern, perhaps with some flexibility in the middle, matches another. This could be a numerical sequence, a code snippet, or even a particular kind of behavior, you know?
For instance, in a very practical sense, if you think about searching for information, a pattern like this could be a search query looking for files that start and end with 'x' and have a certain number of characters in between. Or, it could be a way to describe a specific type of identifier. This sort of pattern recognition is, frankly, something we do all the time, even if we don't always put it into words. It's how we sort through things and find what fits a particular mold, which is quite useful, apparently.
The beauty of this abstract pattern is that it lets us think about equality beyond just exact duplication. It allows for a kind of conditional sameness, where certain parts must match, but others can vary. This is a bit like how a `SUMIF` function works in a spreadsheet, as mentioned in some of the community discussions about data, you know, where you sum values only if they meet a specific condition. The condition itself defines the "equality" for that particular calculation, which is really quite clever.
Finding Equivalence in Data and Information
In the vast sea of data we deal with every day, figuring out when "x*xxxx*x is equal" becomes a really important task. Think about how much information we process, from online communities to technical specifications. For example, when comparing the performance of different graphics cards, like the RTX 5050 benchmarks from TechPowerUp, as some data suggests, we're looking for what makes one card "equal" to another in terms of capability or output at certain resolutions. It's not about being identical, but about reaching a similar performance level, which is a kind of functional equality, you see.
Data analysts, for instance, are constantly looking for these kinds of equivalences. They might use specific algorithms to spot recurring patterns in large datasets. This could mean identifying customer behaviors that are "equal" in their outcome, even if the individual steps taken by each customer were a bit different. It's about finding the common thread, the underlying structure that makes disparate pieces of information comparable. This helps us make sense of things and, actually, predict future trends, which is pretty neat.
Even in areas like managing digital content, where communities are dedicated to discussing things like digital piracy and its legal advancements, the concept of "x*xxxx*x is equal" comes into play. It's about recognizing when a piece of content is equivalent to another, perhaps in its form or its function, even if it has been altered slightly. This sort of pattern matching helps define rules, identify violations, or even just categorize things effectively. It's about bringing order to what might otherwise seem like chaos, more or less.
Practical Tips for Spotting Patterns
- Look for Repetition: Are there elements that appear over and over? This is, basically, the first clue.
- Identify Variables: What parts of the pattern can change, and what parts stay the same? Understanding this helps define the "x" and the asterisks.
- Context is Key: What does the pattern mean in its specific environment? A pattern in a financial report will mean something very different from one in a biological sequence, you know.
- Use Tools: Software and scripts can help automate the search for complex patterns, especially in large amounts of data. This is, apparently, how a lot of big data analysis gets done.
Systems and Consistency: Where Equality Really Matters
The idea of "x*xxxx*x is equal" is also very important when we talk about how systems work and how we maintain consistency within them. Think about online platforms, like the kind of question-and-answer community 知乎 (Zhihu) describes itself as, where high-quality content and user interactions are key. For such a platform to function well, certain behaviors or content types must be treated as "equal" under specific rules to ensure fairness and quality. If everyone follows the same guidelines, the experience is, actually, consistent for everyone, you see.
In technical systems, this concept is even more concrete. When a system processes data, it often needs to verify if an input matches a predefined "x*xxxx*x" pattern to ensure it's valid or to route it correctly. For instance, when you log into a web service, like the 闲鱼 (Xianyu) web page, the system checks if your login details match what's stored. Your input has to be "equal" to the stored credentials for access to be granted. This is, in a way, a very strict form of equality, isn't it?
Maintaining consistency means that if you perform the same action under the same conditions, you should get an "equal" or predictable result. This is fundamental to reliable software and hardware. When we hear about "thrilling updates" or new features being rolled out, as some announcements suggest, a lot of work goes into making sure these changes don't break existing "equalities" within the system. It's about ensuring that the new elements integrate smoothly and that core functions remain stable, which is, obviously, a big deal.
Building Reliable Systems
- Clear Definitions: Define what "equal" means for each part of your system. Is it an exact match, or is there some flexibility?
- Standardized Processes: Ensure that actions that should produce "equal" outcomes follow the same steps every time.
- Testing for Equivalence: Regularly test if different inputs or conditions lead to the expected "equal" results. This helps catch problems early, you know.
- Documentation: Keep records of how "equality" is defined and maintained within the system. This is, basically, for future reference and troubleshooting.
Human Perception of Sameness: More Than Just Numbers
Beyond technical systems and data, our own human perception plays a significant role in how we interpret "x*xxxx*x is equal." We're naturally wired to find patterns and make connections. Think about reacting to a movie trailer, like the "Ago tu bian yingxiong x (to be hero x)" trailer reaction mentioned. People watch it and decide if it's "equal" to their expectations, or if it's "equal" to other movies in a genre, or if it's "equal" in quality to previous works by the same creators. This is a very subjective kind of equality, isn't it?
Our brains are constantly trying to find similarities and categorize things, which is, in a way, a form of seeking equality. We group objects, ideas, and experiences that share common traits, even if they aren't perfectly identical. This helps us make sense of the world and learn from past experiences. It's why we can recognize different fonts as being the "same" letter 'A', or different voices as being the "same" person speaking, even with variations in tone or speed. It's a subtle but powerful cognitive process, you know.
This human ability to perceive equivalence, even with variations, is what allows for creativity and adaptation. It's not always about strict mathematical equality, but about a more fluid, contextual sameness. It's how communities form around shared interests, even if individual members have unique perspectives, as seen in various online groups, including those dedicated to creating various forms of content. They find their "equality" in a common purpose or passion, which is, frankly, quite amazing.
Common Questions About Patterns and Equality
What makes a pattern truly "equal" to another?
Well, what makes a pattern truly "equal" really depends on the specific rules or context you're using, you know? Sometimes, it means an exact, character-for-character match, like when you're checking a password. Other times, it means a functional match, where different inputs lead to the same result, or where certain parts of the pattern are flexible while others must stay the same. It's about defining the conditions for sameness, which is, basically, the core idea.
How do computers identify complex patterns like "x*xxxx*x"?
Computers identify complex patterns using algorithms that are, actually, designed to look for specific sequences or structures. They can use techniques like regular expressions, which allow for wildcards (like the asterisks in our pattern) and define character sets. This lets them match patterns even if there are variable parts. It's all about breaking down the pattern into rules that the computer can follow, which is, apparently, how a lot of searching and filtering works.
Why is recognizing equality important in everyday life?
Recognizing equality is important in everyday life because it helps us make sense of things, make decisions, and interact with the world around us. It's how we categorize information, understand rules, and predict outcomes. From knowing that two different brands of milk are "equal" in their nutritional value to understanding that a certain behavior will always lead to an "equal" consequence, it helps us navigate our experiences, you know. It's, in a way, a fundamental part of learning and adapting.
The journey into understanding what "x*xxxx*x is equal" means takes us through fascinating territory, from the precise rules of data analysis to the fluid nature of human perception. It shows us that equality isn't always a simple, binary concept. Instead, it's often conditional, contextual, and sometimes, even a little bit subjective. It's about finding those points of connection, those shared characteristics that allow us to compare, categorize, and ultimately, make sense of the information and experiences that come our way. To learn more about data patterns on our site, and to link to this page understanding equivalence.
- Viralkandcom
- Hanalei Swan The 30m Shark Tank Deal She Turned Down Ndash What Happened
- Faith Adanza
- Vegmovies
- How Much Does Patience Wolfe Make
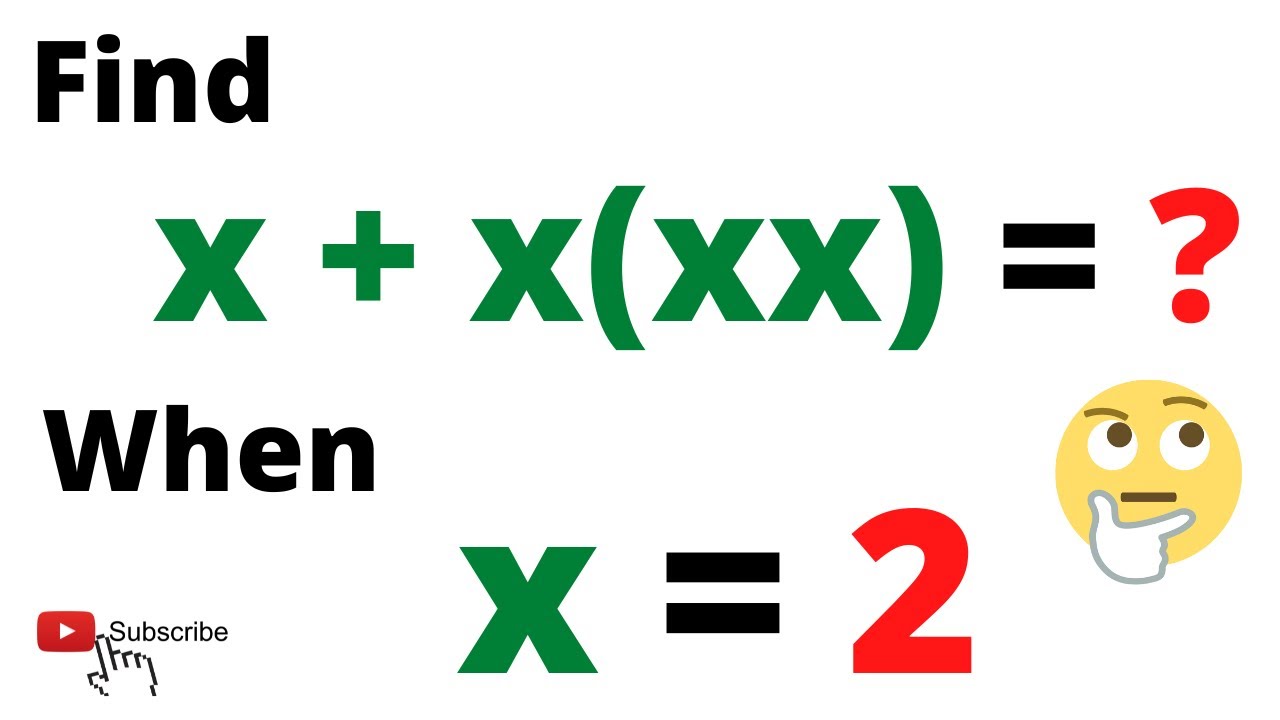
The value of x + x(xx) when x = 2 is: | Find the Answer in Seconds
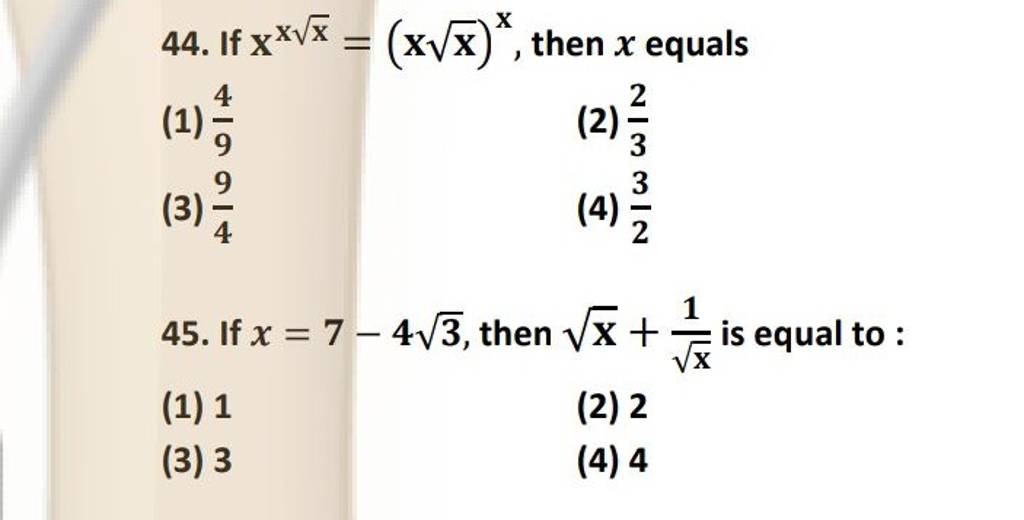
If x=7−43 , then x +x 1 is equal to : | Filo

x*x*x is Equal to | x*x*x equal to ? | Knowledge Glow